Understanding revenue organizations
Introduction
Cargo's integration capabilities with CRM and outreach tools, such as Salesforce, Hubspot, and Slack, significantly improve lead routing processes across multiple platforms within a single interface.
This feature introduces the concept of a revenue organization, making it accessible at both the node and workspace levels.
The point is to enable revenue operations professionals to dynamically manage configurations that would traditionally need to be handled through manual adjustments across multiple product interfaces.
Allocation node
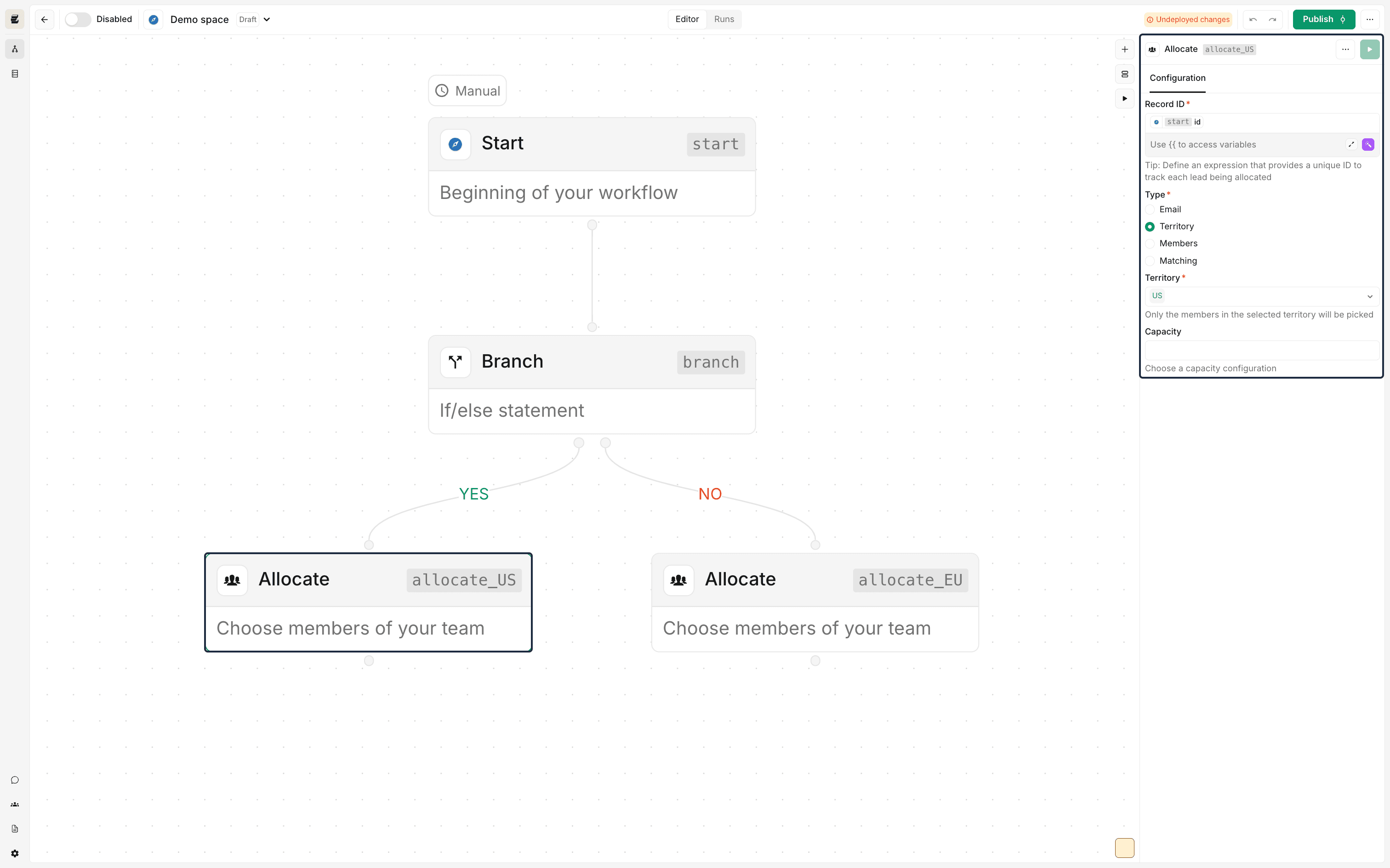
The allocation node allows assigning leads and managing the distribution of workloads for territories and/or team members across different integrated tools.
For instance, if you need to assign a lead to a team member named 'Joe Bloggs' in both Outreach and Salesforce, you can easily select Joe within the allocation node and carry out the assignment. See this guide for a practical demonstration of this node in action.
You will notice that the allocation node always requires an expression that define a unique ID for the record being allocated to a member, in order to track the individuals allocations and ensure that multiple capacity settings are respected.
This node can also be used to surface the unique IDs of available members within these tools, which can be very helpful to send alerts and dynamically allocate across different platforms.
Territory and capacity settings
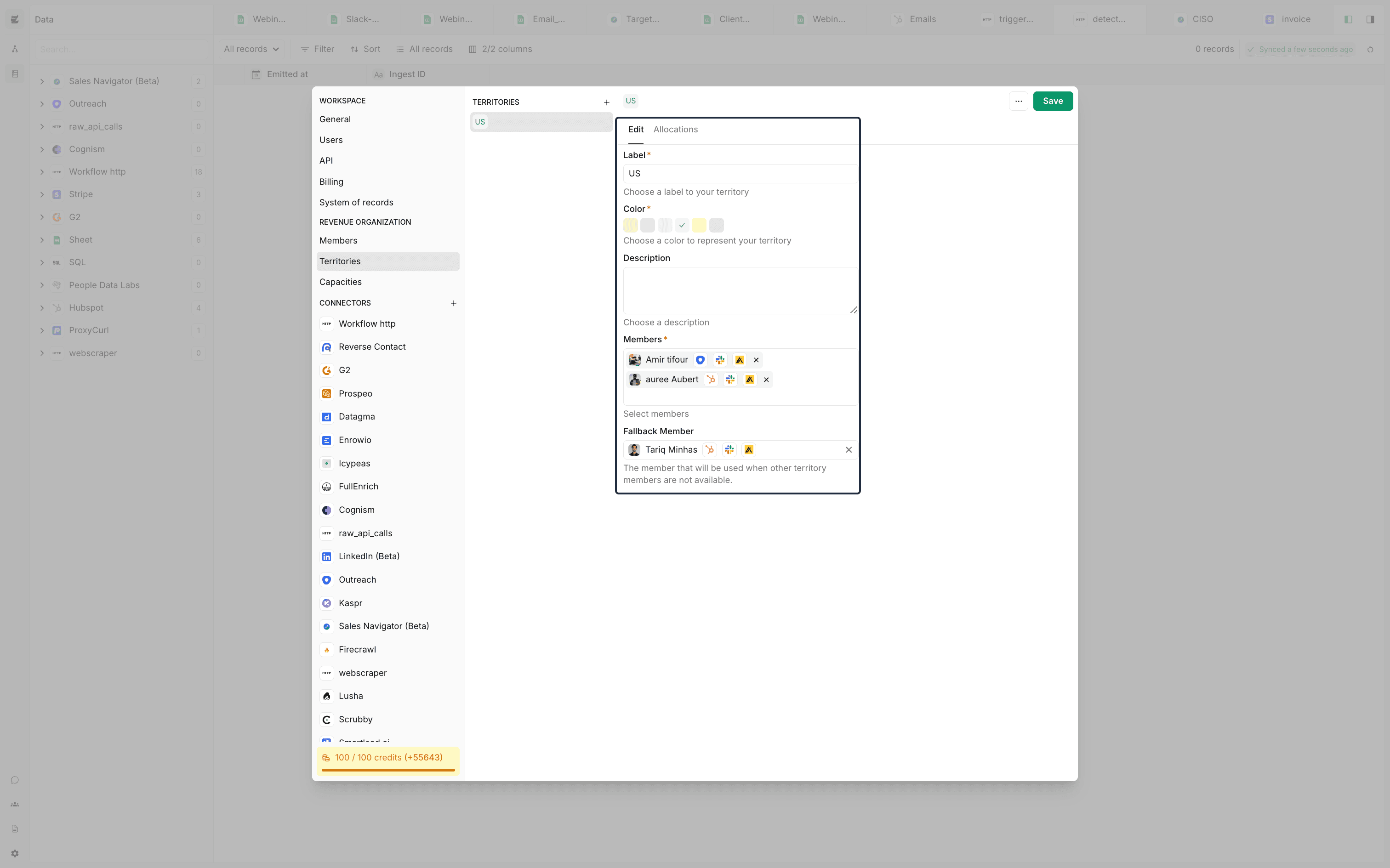
Territories and corresponding capacities in Cargo facilitate the optimization of lead distribution, ensuring workloads are evenly balanced across team members using the capacities feature (see a practical demonstration). Note that this allocation is done across the platform, and is not specific to the specific workflow from where it is initiated.
Cargo provides comprehensive controls for managing territories, which are essentially groups of team members organized by common assignment criteria (see a practical demonstration). This organization allows for lead distribution to be targeted according to specific geographic or sectoral focuses, ensuring a strategic approach to lead engagement.
A key feature within this framework is the concept of a fallback member, designed as a safety net to prevent any lead from being overlooked due to capacity constraints. This fallback member is activated when the primary assignee reaches their maximum capacity, thus maintaining continuous engagement with leads.
Allocation interval and model mapping
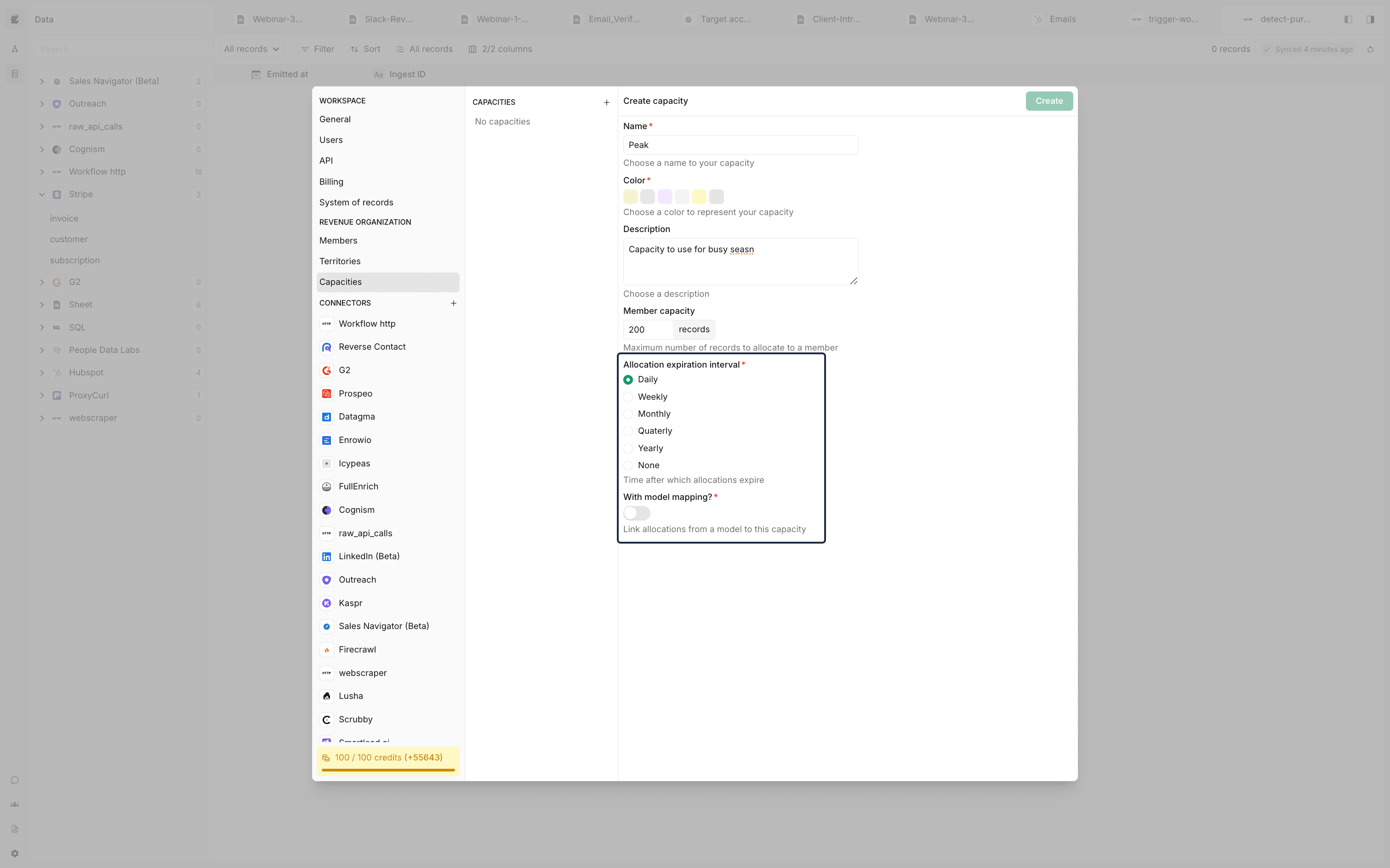
The allocations feature maintains a tally of lead distribution among team members, categorized by specific criteria, which aids in monitoring and adjusting the lead assignment strategy. Users can prevent the overloading of team members by defining a maximum capacity for lead assignments, ensuring no individual is overwhelmed with too many leads.
Capacity settings do not persist indefinitely; the allocation interval defines the maximum time period for which these settings can be enforced before they reset. Additionally, model mapping allows for the adjustment of capacities based on filters applied to specific models within the workspace, enabling users to create dynamic rules for managing allocation capacities effectively.